Renewable energy is playing an expanding role in satisfying total energy demand globally. However, in Iraq, the role of renewable energy is very modest. Reforming existing energy policies is necessary to promote Renewable Energy. Current energy policies discourage renewable energy and subsidize fossil energy. Such reforms will bring appreciable environmental and economic advantages. It is also to be noted that Iraq is characterized by a high number of sunshine hours most of the year that makes solar energy a very attractive and economic form of realizable renewable energy.
In the first part of the post, I will discuss environmental and economic advantages that can be brought up by Renewable Energy. In the second part, I will discuss the role of financial and regulatory policies in promoting Renewable Energy and the energy policy reforms needed in Iraq to tap this important energy resource.
Renewable Energy Brings Environmental and Economic Advantages
Renewable Energy use brings several environmental and economic advantages. This fact has already linked renewable energy to sustainable development and green growth economic development models. Today, Renewable Energy occupies a central role in the development plans in many countries and should have a similar role in Iraq’s development plans. Renewable technologies are environmentally superior to fossil energy
Fossil fuels produce pollution from incomplete combustion (such as Carbon Monoxide) and impurities (such as sulfur oxides). Such products are bad for the environment and public health. In addition, produced Carbon emissions contribute to Climate Change as has been proven by an array of scientific evidence. Thus leading nations are working collectively to set a global regime to limit Carbon emissions. Renewable energy plays a central role in any strategy to limit carbon emissions as part of climate change mitigation efforts.
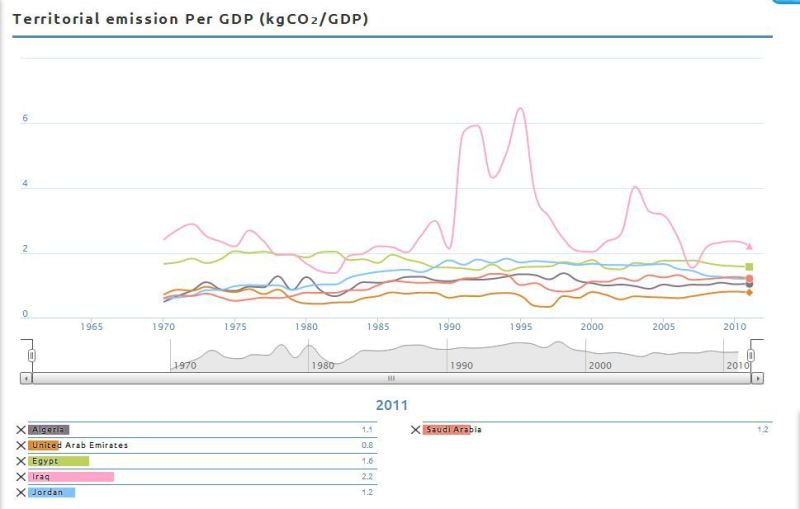
Iraq suffers from several environmental problems due to decades of wars and environmental neglect. According to World Bank Carbon Emission data Iraq produced a total of 122 Mega ton of CO2 in 2012 which amounts to 3.7 ton per capita. Total CO2 emissions are growing at a rate of 6%. That is doubling every 12 years. Iraq has the highest rate of CO2 emissions per GDP in the region (see figure below). growth in GDP and population would increase CO2 emissions to even higher levels.
Carbon emissions can be controlled by gradual shifting of energy production to renewable sources of energy.
On the other hand, Renewable Energy sources convert energy from abundant forms of energy, such as solar energy, to useful forms such as electricity, without pollution or carbon emissions. That is, Renewable Energy is an absolutely clean energy source. Shifting energy sources from fossil to renewable gradually is a necessary step if we want to limit Climate Change and improve Iraq’s environment.
Renewable Energy is affordable
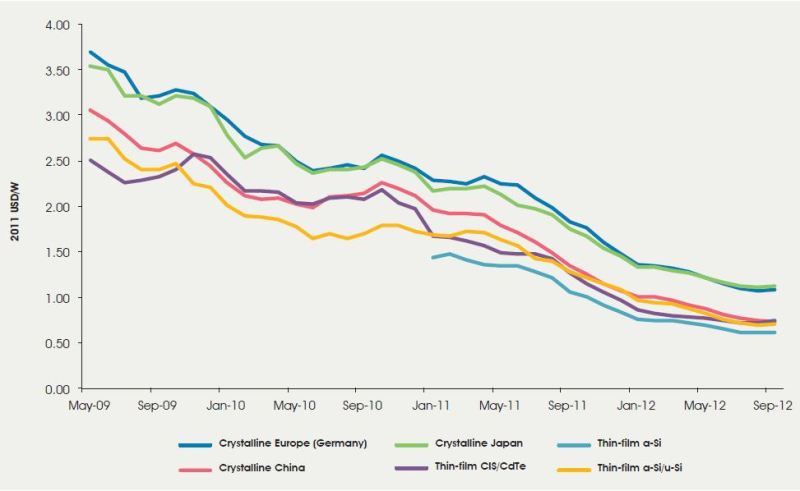
The second fact about Renewable Energy is that it has become affordable economically compared to fossil energy. Technology development and innovation coupled with the economies of scale were successful in bringing down the cost of renewable energy close to that of fossil energy. The following diagram shows the drop of solar panel costs in a time span of lower than three years.
This drop in costs produced a surge installing Solar PV panels globally. PV Solar panels became competitive to conventional fossil energy sources in many parts of the world.
In Iraq, with a yearly average of about 3300 hours of the sunshine, the energy produced from Solar sources are economical, taking into consideration that countries in Europe, such as Germany with only 900 sunshine hours per year succeeded in installing more than 20000 MW of Solar panels. That is with the same investments, solar energy produced in Iraq would be more than 3 times that in Germany.
In addition, Renewable Energy has proven to offer more jobs than those it replaces from fossil energy. It is well-known that the conventional energy sector has low employment rate. Data from developed countries point to about four jobs are created in the Renewable Energy sector for every job replaced in fossil energy. That is good news that makes renewable energy attractive for countries where unemployment is an economic problem. That applies to Iraq with high unemployment especially in the youth age group and among university graduates.
Technology developments have contributed to making Renewable Energy (especially Solar energy) competitive with conventional energy sources economically. Besides, Iraq’s weather and long sunshine hours contribute positively to the economics of Solar energy. In addition, Renewable Energy in Iraq will also contribute to economy diversification and job creation, both are important national economic priorities.
Energy policies in Iraq favor fossil fuel
I will explain here energy subsidy in Iraq’s Energy policy. Then discuss subsidy’s impact on Iraq’s domestic Renewable Energy market and consumer behavior.
Traditionally, the Iraqi government through its social policies has protected citizens from fluctuations in oil prices in the global market. Oil and derivatives’ prices are fixed for about a decade and didn’t reflect the global rise in energy prices. Electricity prices were left without any adjustments for a long period too.
The International Energy Agency IEA estimates the cost of energy subsidies in Iraq to be $ 22B in 2012. IEA estimates subsidies would total $ 65B in 2035 if present policies continued. Subsidies are estimated based on direct cost or missed export opportunity. That includes only oil and derivatives. For electricity, prices in Iraq are at about 1.7 cents/KWh, compared to 13-17 cent in neighboring countries. that is about 10% of its real cost. Subsidies reduced the cost of different forms of energy to the consumer by 60-90% of their real prices depending on the energy product considered.
Such subsidies of energy distort any real economic assessment of renewable energy economics when compared to fossil energy. Renewable energy would look highly expensive compared to subsidized other forms of energy. On the other hand, It is well understood that subsidies cannot be lifted due to social backlash.
To solve this problem, the only possible solution seems to be for the government to subsidize renewable energy at least at the same subsidy levels given to fossil energy. This will level the ground between fossil and Renewable Energy and remove any cost distortions. This should not have any extra cost on the government since any new Renewable Energy generation capacity will replace fossil energy thus saving fossil subsidy. Therefore, subsidies will shift from fossil energy to Renewable Energy keeping total energy subsidies constant. This will allow energy decisions to be based on economics without distortions.
Iraq has been highly interested in Renewable Energy research technologies for since 1985 when the first research center was established. Today, Renewable Energy research is active in most Iraqi universities. However, existing energy policies were the major obstacle to innovation in this field and policy reform is necessary.
Financing Renewable Energy plants
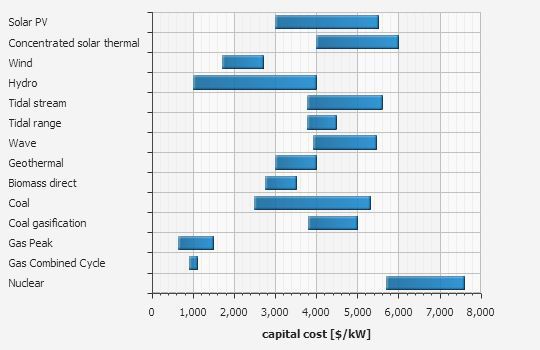
Renewable Energy plants require new financing schemes. Their financing differs considerably from conventional energy installations. Renewable Energy, especially Solar energy, requires high capital costs compared to fossil plants that are needed upfront. Capital cost depends on the technology used. The following figure gives an idea of capital cost associated with different types of Renewable Energy plants.
Fossil energy generation capital costs are of the order of $800-$1000 per kW, while we can see that Solar PV technologies may cost more than 5 times this value. Of course, that will be compensated by the lower running cost of Solar PV compared to fossil fuel generator. Therefore, financing of Renewable Energy plants is very important. Sometimes the upfront cost of such installations becomes the decisive factor and not the economics.
Such influence is noticed with households when considering installing domestic Solar PV. Such installations did not succeed in Iraq in spite of the severe energy shortage during the past decade. The obstacle was the lack of ability to financing the capital cost. Buying a gasoline generator would cost 5% of a Solar PV system with comparable capacity. But economic considerations, in the long run, would favor Solar PV to a domestic gasoline generator.
In developed countries, energy financing schemes are offered by banks and supported by the government. Such schemes would lower initial costs and repayments can be made from savings from eliminating fuel cost with the additional overall cost savings. Such financing schemes are available as energy loans targeting different sectors in many countries. Even micro-loans were established successfully to support renewable energy in some underdeveloped countries.
Often governments take the initiative to offer credit to finance Renewable Energy units. Here I will give the link of two programs as examples. The first is EnergyLoan in the USA and the second is BEECIFF program in Bulgaria, supported by European Investment Bank. Similar programs exist in most advanced countries and such programs contributed to the increasing share of Renewable Energy in their energy portfolio. It is obvious that Iraq can learn from such success stories.
New Renewable Energy policies in Iraq will help to overcome resistance to using Renewable Energy because of fossil energy subsidy and need of special financing programs.
After showing these facts, it is clear that Renewable Energy brings with it important environmental advantages that will be reflected positively on society and sustainability. Iraq has relatively high CO2 emissions per GDP compared to other countries in the region. Renewable Energy would contribute to reducing these emissions in Iraq.
Renewable Energy is already economic and does not need expensive extra resources. For Iraq, Renewable Energy will also contribute to important economic goals such as economic diversification and job creation for new university graduates. However, to promote such technologies Iraqi need to reconsider its energy policies. Energy policies in Iraq need to address at least the following two points:
- Renewable Energy needs to be subsidized at least at a level similar to subsidy applied to fossil energy. This will stop the present uneconomical bias to prefer fossil energy to Renewable Energy.
- Iraqi should start programs in coordination with local banks to provide financing opportunities for Renewable Energy projects in different sectors such as households and industry.
When energy policies are reformed to favor Renewable Energy in Iraq, innovation in the Renewable Energy sector will have the potential of playing a much bigger role in Iraq’s energy economy and improve the environment for Iraq’s citizens. Working to reform energy policies will not only improve the environment and offer clean energy to the public but also create more jobs.
Did I miss anything? Or any extra information or comments would you like to add here? You can always use the comment section below to let us know of your ideas.
Samir Raouf
Related articles
- Energy in Iraq’s National Development Plan
- Oil-Exporting Economies at a Crossroad: Restructure or Risk Economic Growth
- Science and Innovation in Iraq’s National Development Plan 2013-2017
- Paris Climate Agreement 2015: MENA Oil Exporters Made the Right Choice, but More Is Necessary
- Reforms in MENA Countries: Are We Missing Science in Iraq’s Reform Agenda?

Thank you for the valuable article…
Many years ago, I thought the renewable energy is like games to waste money for the oil countries, but later I’ve understand this game when I read a report for the renewable energy in US. In US, the wind resources produce nearly 10 times the country’s existing power needs and currently over 400 american manufacturing plants build wind components, towers and blades. Besides, the solar installations in the United States exceed 3,100 MW, enough to power more than 630,000 homes and employed more than 100, 000 Americans.
LikeLike
Dear Dr. Ghassan,
Thanks for sharing the info,
The following link from EIA gives details about US energy mix including types of renewable energy. Renewables in US now account for 13% of their total energy, while petroleum accounts for only 1% of total energy!
LikeLike
Dear Mr. Samir Raouf.
First of all, I agree with you in your considerations for renewable energy in Iraq. It is difficult, and the Iraqi government faces many of the same challenges that Europe had years ago. Furthermore they have the challenge, that the infrastructure has lacking due to the years of war.
Based on personal experience, having worked on renewable energy projects in Iraq during the last 3 years, I would like to make the following comments at your post.
In my experience, some of the main reasons for the interest / expansion of renewable energy supply in Iraq is absent, are due to the facts that:
1. Lack of electricity.
There is a huge lack of electricity – the amount of produced electricity is not covering more than roughly 50 % of the demand.
To fulfill the public demand, the focus are on plants fueled by either oil or gas, is higher than it is on renewable energy options. That is due to the fact, that building these plants, on the short lane, is cheaper and faster to build. And because that the access to oil is easy, and cheap.
Not taking into consideration, that the oil instead could be sold, and the profit could be used to make renewable energy plants.
2. Security.
The security situation in Iraq are still very uncertain. Even though the security situation is improved during the last 3 years.
This means, that it is difficult to explore the truth potential for areas that are suitable for renewable energy sources.
3. Remote areas
There are a lot of areas that are not connected to the public grit. This means that solutions used are more advanced, compared to solutions used in e.g. Europe.
4. Long decision making.
The process seems long, and structure regarding decision making seems very opaque.
5. Eeconomics / finance
Due to the above, it seems very difficult to attract foreign capital to developing renewable energy solutions.
The above is a very short description, and if you have any questions, or need a deeper explanation, please do not hesitate to contact me.
Yours Sincerely
Allan Lindgaard Nielsen
LikeLike
Dear Mr. Allan Lindgaard Nielsen,
Thanks for sharing your thoughts and experience in Iraq. You raised important points specific to Iraq’s situation.
I have a comment about your point concerning economics/financing. I agree with you as far as foreign capital investment is considered. However, another area where there is an opportunity is small PV panels (or solar PV- Wind combo) that can be used by households. Lack of sufficient electricity and high prices of electricity from private neighborhood generators create an economically attractive case for such systems. However, without proper financing scheme the initial cost may seem very high and becomes an obstacle.
Suitable financing schemes are available in many countries such as US and Germany where many households partially cover their energy needs from such household systems and the total capacity from such systems comprise an appreciable ration of total energy consumption.
Samir Raouf
LikeLike